LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory)
LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory)
- LSTM is a type of RNN architecture that is widely used for sequnce modeling task
- LSTM overcome RNN limitation(vanising gradient) by introducing a memory cell and three gating mechanisms.
- Memory cell in LSTM allows to store and access information over long sequence
- LSTMs use a series of gates which control how the information in a sequence of data comes into, is stored in and leaves the network. they are -
- forgot gate
- input gate
- output gate
Application
- NLP task- named entity recognition, sentiment analysis, machine translation etc.
- Speech Recognition - automatic speech recognition, speech-to-text conversion etc.
- Time Series Analysis and Forecasting - stock market prediction, weather forecasting etc.
Architecture
Forget gate layer
First step in the process is Forgot gate. This gate telling the LSTM how much information keep from previous state. Output of this gate is between 0 and 1. Output of this forgot gate multiply with previous LSTM output. 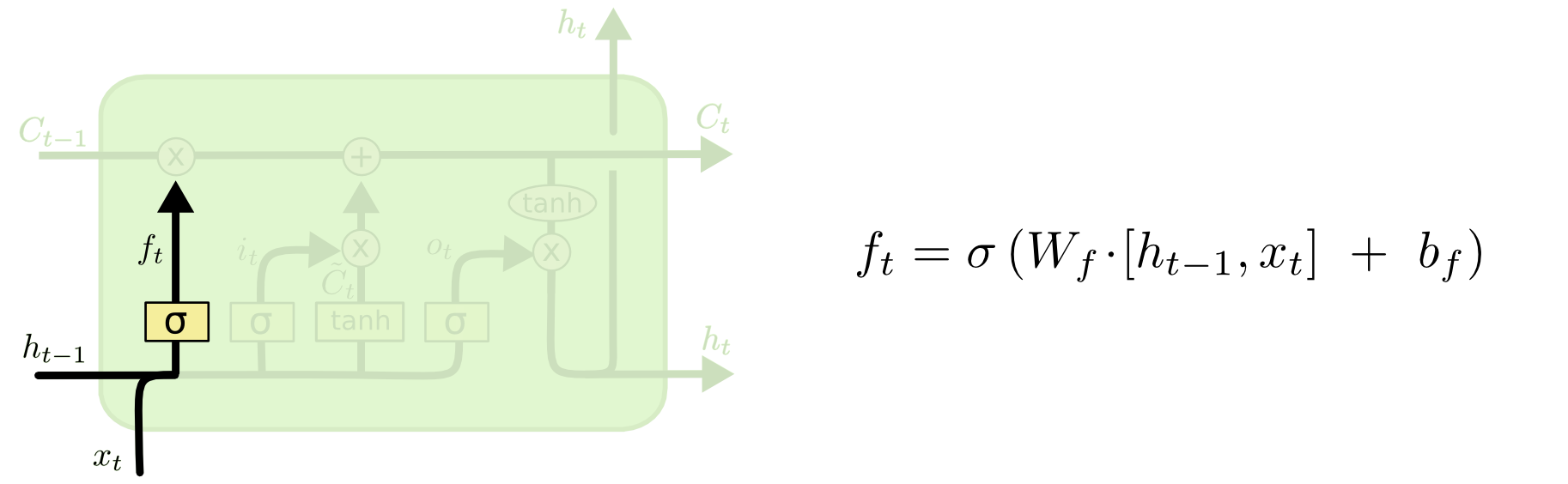
output of forgot gate is 0 implies -> Forget all previous memory
output of forgot gate is 1 implies -> Keep all previous memory
output of forgot gate is 0.5 implies -> Keep some of previous memory
Input gate layer
Goal of this step is how much information take from new memory. This sigmoid layer is call input gate decides which values we’ll update.
output of forgot gate is 0 implies -> Didn’t take anything from generated memory
output of forgot gate is 1 implies -> Take anything from generated memory
output of forgot gate is 0.5 implies -> Take partially from generated memory
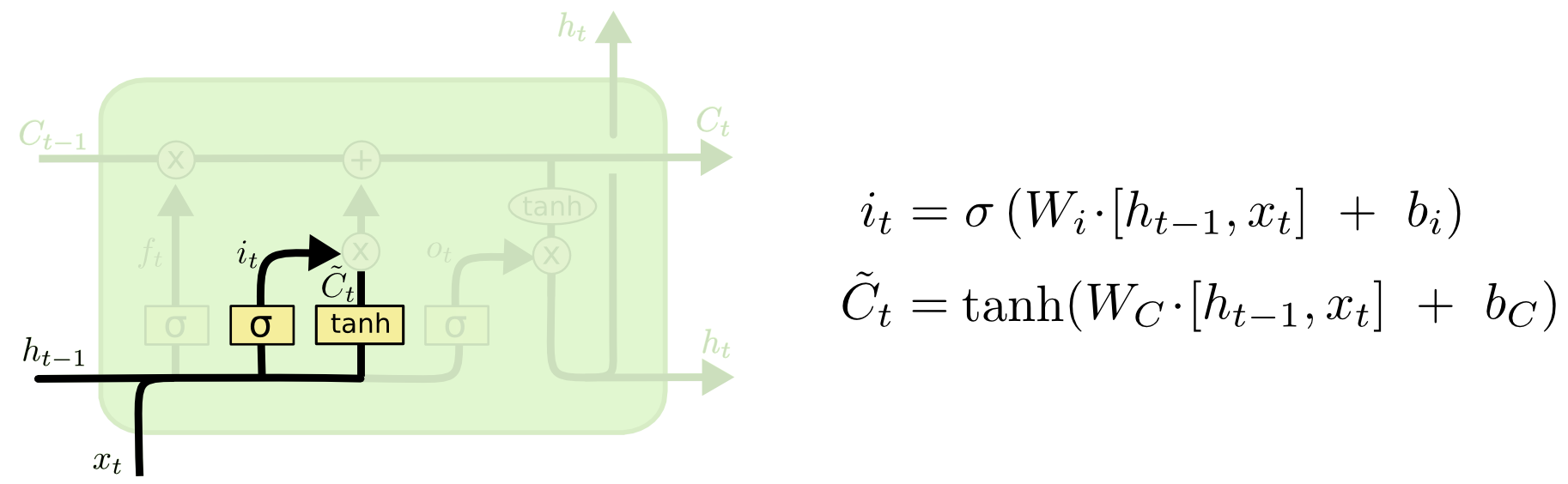
The new memory network is a tanh activated neural network which has learned how to combine the previous hidden state and new input data to generate a ‘new memory update vector’. This vector essentially contains information from the new input data given the context from the previous hidden state
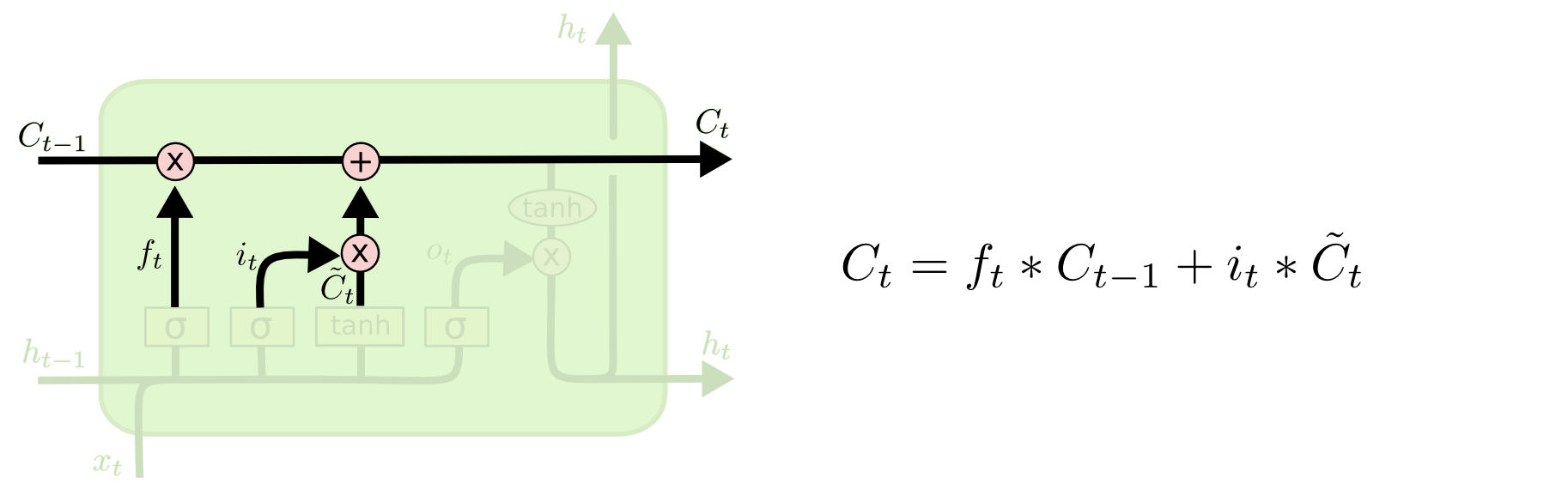
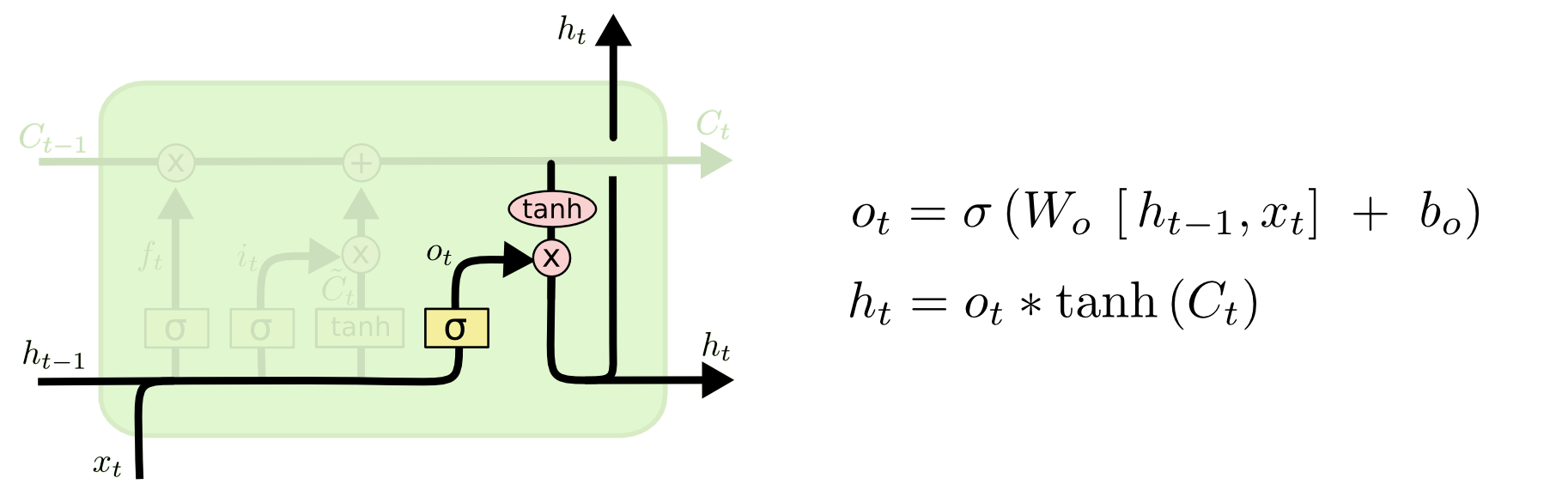
Output Gate
The output gate, deciding the new hidden state. - First, we run a sigmoid layer which decides what parts of the cell state we’re going to output. - Then, we put the cell state through tanh and multiply it by the output of the sigmoid gate, so that we only output the parts we decided to.
Drawbacks LSTM
- Computational Complexity
- Training Time
- Difficulty in Hyperparameter Tuning
Reference
- http://colah.github.io/posts/2015-08-Understanding-LSTMs/